The field of Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A) is constantly evolving, necessitating well–defined processes to ensure efficiency and effective navigation of uncertain times. As companies strive to offer the highest value services to their customers at speed, FP&A teams must keep up with advances in digitization, technology and formal procedures.
In a sense, the FP&A process flow can be broken down into three key components: strategic planning, budgeting & forecasting, and data analysis – each with its own set of processes for successful outcomes.
To ensure your process is efficient and up–to–date with industry standards, let's dive deeper into what each component entails regarding FP&A process flow.
The Step-by-Step FP&A Process Followed by Modern Teams
Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A) is a critical component of any business that entails gathering, examining and interpreting financial information to make informed choices. To guarantee efficiency and accuracy, modern teams adhere to a structured approach.
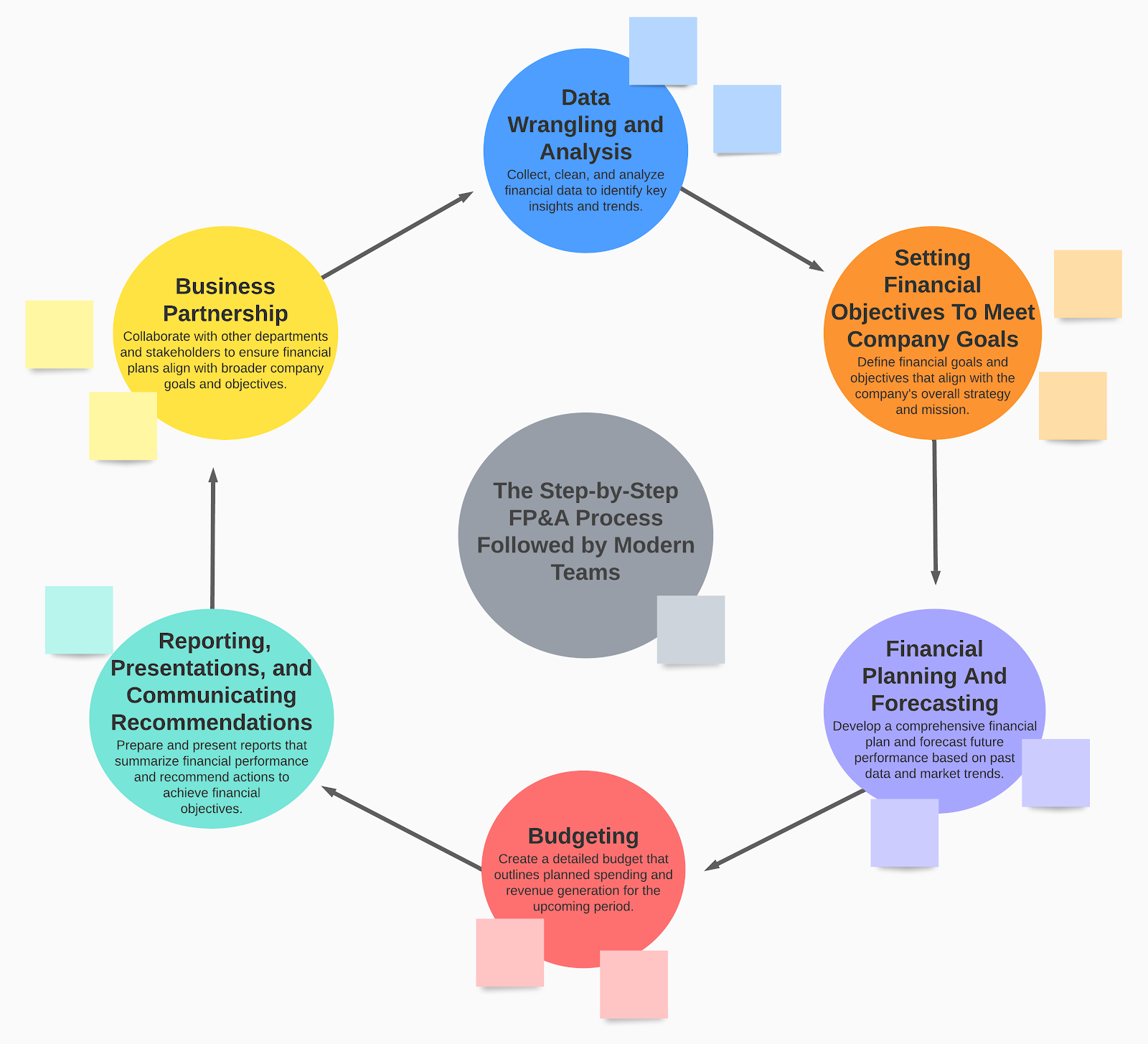
Data Wrangling and Analysis
Data wrangling no longer requires manual labor and tedious hours. Automation, integrations, data connectors, and other technologies have revolutionized the process – making it far easier to manage than before.
To ensure accuracy and reliability in a single source of truth while minimizing discrepancies in the system, data must be collected from various sources such as ERP systems, data warehouses, and spreadsheets, while also establishing a dictionary with cross–functional stakeholders for consistency across all departments.
Security measures should also be put in place to protect sensitive data; these may include encryption and secure user authentication protocols, as well as access control to ensure that only authorized personnel can view or modify the information.
Setting Financial Objectives To Meet Company Goals
Once the data has been scrutinized, FP&A must then devise financial objectives that are in line with the company's wider aims and strategies. This necessitates a comprehensive review of past performance, prevailing market conditions, and any potential impediments to ensure attainable revenue, outlay and profitability goals.
It is essential for FP&A teams to collaborate with other departments within the organization, confirming that these objectives align with broader business strategies. By doing so, all decisions regarding investments, staffing needs and other core areas of focus are informed by clear financial objectives.
Furthermore, tracking progress throughout the year by analyzing financial reports and contrasting them against budgeted amounts helps identify areas where modifications may be needed. For instance, if sales are lagging behind projected figures, the FP&A team can assess ways of boosting revenue such as implementing new marketing strategies or offering promotional discounts.
Similarly, cost overruns in a particular department can be addressed by looking for ways to reduce expenses without compromising on quality of service.
Financial Planning And Forecasting
Analyzing past financial data, recognizing trends, and forecasting future performance are all essential elements of the FP&A process. Effective financial planning and forecasting is key to success; it's necessary for developing a sound financial strategy and making informed decisions about resource allocation, capital investments, and growth opportunities.
Unfortunately, traditional methods like spreadsheets can be time–consuming and complex. To address these challenges, many modern FP&A teams are turning to financial planning software to streamline the process and increase accuracy.
One example is Pigment, which was implemented by Gorgias – a customer that experienced serious blockers to scalability using spreadsheets.
Co–building with Pigment resulted in a full month of time savings during their 2023 budget planning and enabled seamless collaboration between finance and department leads.
Its value lies in its ability to allow teams to work collaboratively, automate calculations, and visualize data in real–time – all key aspects for successful financial planning and forecasting.
Modern FP&A teams can use driver–based forecasting to create accurate financial forecasts. This approach focuses on linking key business drivers to financial outcomes in order to create detailed forecasts.
Predictive and prescriptive forecasting takes this one step further, utilizing historical data and employing statistical algorithms to not only predict future performance but also provide prescriptive insights.
Exception–based forecasting emphasizes the identification of anomalies and exceptions, which can then be used to make predictions about future performance.
Moving average forecasting is a method that calculates averages over time to better understand trends and forecast future performance more accurately.
Alternatively, linear regression can be used for financial planning and forecasting which involves creating a linear equation from historical data in order to predict future performance.
Scenario planning
Scenario planning is another important method of analyzing different scenarios to better understand how changes in the market, economy or business operations may impact financial performance. This approach helps FP&A teams prepare for unexpected events and make informed decisions about resource allocation and risk management.
Some examples of scenarios that FP&A teams should consider include economic downturns, technological advances, currency fluctuations, industry disruption and more.
For example, when it comes to workforce planning, FP&A teams can use scenario planning to evaluate various headcount reduction assumptions and compare them with current workforce strength. This helps identify areas of risk and create contingency plans that ensure the business is prepared for any eventuality.
Similarly, sales capacity planning allows FP&A teams to assess different ramp time and headcount freeze variables in order to generate more precise sales quota forecasts. This enables organizations to optimize sales operations and revenue forecasting accuracy.
Strategic operations involve scenario planning, where FP&A teams can develop P&L targets based on a percentage of revenue and allocate functional goals to cost centers accordingly; this ensures that the financial strategy is in line with business objectives, facilitating long–term sustainable growth.
Continuous planning
Continuous planning is another approach used by modern FP&A teams to optimize financial planning and forecasting. This involves ongoing monitoring and adjustment of financial plans and forecasts to reflect changes in the business environment.
Benefits include improved decision–making accuracy, better visibility into operational performance metrics, quicker response time when responding to market events or customer demands, reduced risk exposure due to enhanced data quality control processes, and faster cycle times for updating plans and making decisions.
Continuous planning enables FP&A teams to take ownership of financial performance and drive accountability across the organization.
Additionally, it facilitates improved collaboration by increasing organizational visibility and communication – allowing teams to respond effectively to changes in the market or business environment.
Budgeting
Creating a financial strategy for the upcoming year or period is an essential component of Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A). This strategy must be tailored to reflect an organization's objectives and goals in order to ensure effective budgeting.
The process of budgeting can be complex and time–consuming, but modern finance teams have sought to simplify it by implementing automation software such as Pigment.
Loggi, a Brazilian technology company providing delivery services, was able to reduce its data aggregation time with Pigment while also involving cost center managers in the budgeting process for greater precision in business evaluation and access rights control. This enabled stakeholders to make better decisions more quickly and efficiently – fostering alignment within the organization.
Zero–based budgeting (ZBB) is another approach that has been gaining traction among modern finance teams. It focuses on allocating resources based on need rather than basing them off previous funding levels, requiring organizations to construct their annual budgets from scratch each year and emphasizing the connection between company spending and strategic objectives.
This process has five primary characteristics:
- An emphasis on both "how much" a single unit will incur,
- The "why," decisions based on what each unit can offer at a given cost,
- Alignment of individual unit goals with corporate objectives,
- Ready adjustments in the budget if needed, and
- Participation of all levels of an organization in decision-making.
When planning your budget, it is critical to involve stakeholders from different departments – marketing, sales and operations – in order to ensure that the budget is realistic and aligned with organizational objectives. Cross–functional collaboration can help you overcome potential challenges such as...
- Siloed departments: In many organizations, different departments may work in isolation, without sharing information or collaborating with other teams. This can lead to a lack of understanding of the overall organizational strategy and can result in suboptimal decisions. Cross-functional collaboration can break down these silos and encourage departments to work together towards a common goal.
- Lack of alignment: Departments may have different goals and objectives that are not aligned with the overall organizational strategy. This can result in budgets that do not support the organization's overall strategic direction. Cross-functional collaboration can help ensure that all departments are aligned with the organization's overall strategy and that budgets are developed with this strategy in mind.
- Inaccurate forecasting: Without input from different departments, forecasts for revenue, expenses, and other key financial metrics may be inaccurate. Cross-functional collaboration can help ensure that forecasts are more accurate and realistic by incorporating input from different departments and considering a broader range of factors.
- Inefficient resource allocation: Without cross-functional collaboration, departments may allocate resources in ways that are not optimal for the organization as a whole. Cross-functional collaboration ensures that resources are allocated to support the organization's overall strategic direction and maximize the organization's return on investment.
- Lack of accountability: It may also be difficult to assign accountability for financial results to specific departments or individuals. Cross-functional collaboration ensures that all stakeholders are accountable for financial results and that responsibility is shared across different departments.
Reporting, Presentations, and Communicating Recommendations
To successfully communicate data insights to boards and other stakeholders, crafting a succinct message that aligns with corporate goals is key. Effective communication is essential for making a strong impact and engaging with key stakeholders in board meetings.
To gain buy–in for your business objectives, it's important to develop clear presentations that accurately communicate key insights and recommendations. Unfortunately, the primary obstacle behind ineffective board presentations is often a lack of time.
Data wrangling and inaccuracy, constant refreshes, and narratives lost behind vanity reporting can all lead to meandering and unproductive discussions.
To avoid these issues, modern teams must adopt a strategic approach that focuses on the following steps:
- Ensure data accuracy by integrating with your entire tech stack: Integrating all your data sources into a unified platform can help you eliminate errors and inconsistencies that arise from manual data entry or siloed systems. This approach also enables you to generate real-time insights and make data-driven decisions.
- Enable cross-functional alignment by empowering your teams to collaborate on data: Silos can hinder collaboration and lead to conflicting priorities. As mentioned earlier, by empowering cross-functional teams to access and work on the same data sets, you can ensure everyone is aligned on the business objectives and generate insights that are relevant to all stakeholders.
- Unify your data under overarching business objectives: To avoid meandering conversations, it's essential to focus on the key takeaways that align with your overarching business objectives. Unifying your data under these objectives can help you identify the most critical insights and communicate them clearly to the board.
- Automate your data refreshes to save valuable time: Constantly updating and refreshing data sets can be time-consuming and prone to errors. By automating these processes, you can save time and ensure your data is always up-to-date and accurate.
Business Partnership
The final and pivotal step in Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A) is the establishment of business partnerships, which ensures all organization departments collaborate effectively to reach financial objectives. By collaborating with other departments, such as Human Resources (HR), Sales, Marketing, Accounting, and Data Science teams can obtain key data from each department to analyze performance metrics and identify potential areas for optimization.
This information then feeds back into creating a single source of truth data source which eliminates discrepancies between departments – ultimately enabling organizations to stay within budget.
Data–driven insights provided by the FP&A team help each department make informed decisions based on accurate, up–to–date data; this enables cross–functional collaboration and creates a shared understanding of the organization’s financial goals and priorities.
Pro tip: Keep your FP&A process efficient and up–to–date with industry standards by registering now for our ongoing event, FP&A Week.
Our expert speakers will provide step–by–step guidance on collecting, analyzing, and interpreting financial data to make informed decisions; they'll also cover the latest technologies, software, and tools that modern FP&A teams are using to streamline the process and increase accuracy.
Don't delay; register now to take the first step toward improving your company's financial planning and analysis process.
.svg)

.svg)


.webp)
.jpeg)
.webp)
.webp)

.webp)
